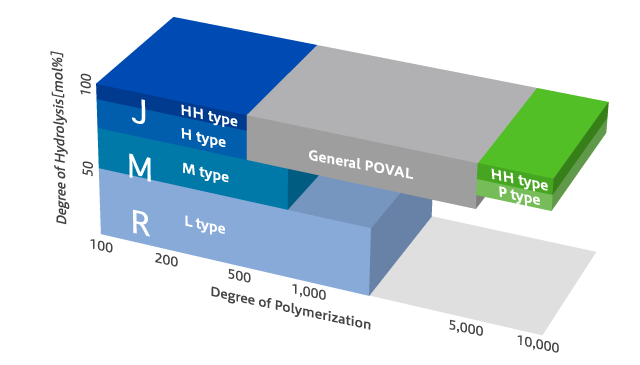
JMR is the general term for resins with a degree of polymerization and a degree of hydrolysis ranges that differ from that of general POVAL.
Ultra low degree of polymerization resins, ultra high degree of polymerization resins and low degree of hydrolysis resins are available.
Ultra low degree of polymerization is a degree of polymerization from 100 to 400, ultra high degree of polymerization is a degree of polymerization from 5,000~8,000(the degree of polymerization of general POVAL is 400 to 4000).
A low degree of hydrolysis is a degree of hydrolysis from 0 to 80 mol% (the degree of hydrolysis of general POVAL is 80 mol% or higher). JMR has many interesting properties that differ from those of general POVAL.
List of Representative Products
Product Series and the Degree of Polymerization and Hydrolysis
Ultra Low Degree of Polymerization Series
| Type/Name | Characteristic | Applications | |
| HH type | JMR-10HH | No melting point Water soluble Low viscosity |
|
| H type | JMR-3H | High melting point Water soluble Low viscosity |
|
| JMR-10H | |||
| JMR-20H | |||
| M type | JMR-3M | Medium melting point Water soluble Low viscosity |
|
| JMR-8M | |||
| JMR-10M | |||
| JMR-20M | |||
| JMR-50M | |||
| L type | JMR-7LO | Low melting point Water swelling |
|
| JMR-10LL | |||
| JMR-10L | |||
| JMR-20L | |||
| JMR-150L | |||
Ultra High Degree of Polymerization Series
| Type/Name | Characteristic | Applications | |
| HH type | JMR-500HH | Water soluble High viscosity High strength High water resistance |
|
| JMR-800HH | |||
| P type | JMR-500P | Water soluble High viscosity High strength |
|
| JMR-800P | |||
Properties
Solubility
JMR’s solubility for solvents differs for each types. A table of the solubilities for representative solvents is given below.
| Pure Solvent | Organic Solvent/Water (60/40) |
|||||||
| Type | Type | |||||||
| Solvent | L | M | H | HH | L | M | H | HH |
| Water (20°C) | – | – | – | – | ||||
| Warm water (50°C to 60°C) |
– | – | – | – | ||||
| Hot water | – | – | – | – | ||||
| Methanol | ||||||||
| Ethanol | ||||||||
| Isopropanol | ||||||||
| Acetone | ||||||||
: Complete dissolution, : Dispersion dissolution (with turbidity), : Undissolved
Thermal Characteristics
Except for the HH Series, JMR has thermal melting. The melting points, constant flow temperatures, decomposition start and decomposition end temperatures for representative products of each types are given in the following table.
| Thermal Characteristics | ||||
| Name | Melting Point [°C]*1 |
Constant Flow Temperature [°C]*2 |
Decomposition Start Temperature [°C]*3 |
|
| L type | JMR-10L | 110 | 115 | 320 |
| JMR-20L | 120 | 125 | 320 | |
| JMR-150L | 190 | 210 | 320 | |
| M type | JMR-8M | 145 | 155 | 300 |
| JMR-10M | 150 | 160 | 300 | |
| JMR-20M | 160 | 180 | 300 | |
| H type | JMR-10H | 170 | 190 | 290 |
| JMR-20H | 180 | 210 | 290 | |
*1 Measured using a Yanagimoto Fine Melting Point Measurement Unit.
*2 Measured at the temperature where the MFR is 10g/10 min at a load of 2.16 kgf.
*3 Read from a Thermo-Gravimetric Analysis (TGA).
*JMR products with a variety of characteristics other than the above are also available upon request.
Applications
Ceramics Applications
Ceramic molding methods that use binders include press molding, tape molding, casting molding, injection molding, and extrusion molding.
JMR can be used with a wide variety of inorganic materials and molding methods, and its properties are especially beneficial for molding oxidized inorganic materials, such as alumina and zirconia.
[Example Applications] Press molding (Compared with general PVOH)
The results of a comparison of the properties and molding performance of a ceramic slurry using alumina and that of general PVOH are given below.
| PVOH | JMR-10M | JP-05 [General PVOH] |
| Slurry concentration(%) | 65 | 65 |
| Slurry viscosity(mPa・s)*1 | 420 | 3250 |
| Spray dry state | good | Difficult to pump fluids |
| D50(μm) | 40 | 45 |
| Appearance of granulation | Perfectry spherical | Perfectry spherical |
| Molded object hardness(N) [Press pressure:40MPa] |
79.0 | 67.2 |
*1 Type B Rotating Viscometer was used(30℃,30rpm)
[Appearance of alumina granules] SEM 500×


