Modified POVAL refers to polyvinyl alcohols containing functional groups other than the hydroxyl and acetate groups found in general POVAL. JVP offers commercially available D Polymer, which contains carbonyl groups, and A Polymer, which contains carboxyl groups. Additionally, various other types of modified POVAL are available upon request.
Specialty POVAL[D Polymer]
D Polymer is a PVOH that has highly reactive “carbonyl groups” as a modified group other than the hydroxyl and acetate groups. The carbonyl group reacts with hydrazide groups and amino groups and in particular it has an especially high reactivity with hydrazide base cross-linking agents, and it can also form coatings and films that do not dissolve even in boiling water. It can be used to produce highly transparent gels.
Structural Formula
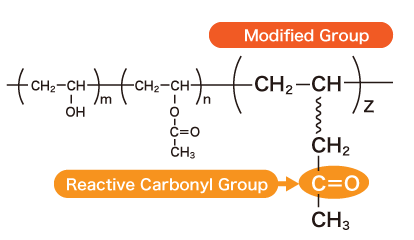
Grade and Quality Specifications
| Grade | DF-05 | DF-10 | DF-17 | DF-20 | DM-17 | DM-20 | ||
| Hydrolysis (mol%) | 98~99 | 95.5~97.5 | ||||||
| 4% aq. Viscosity (mPa·s) | 5.5±2.5 | 11±1.5 | 23±3 | 28.5±3 | 21±3 | 28±3 | ||
| Volatiles (%) | 6.0 or less | |||||||
| Sodium Acetate (%) | 1.5 or less | |||||||
Characteristics
- D Polymer is water-soluble and can be dissolved in water.
- The aqueous solution of D Polymer exhibits excellent viscosity stability and resists gelation even when stored at low temperature for extended periods.
- The incorporated carbonyl groups provide high chemical reactivity.
- Low surface tension in aqueous solutions contributes to superior wettability.
Applications
- Water-resistant coatings in combination with cross-linking agents
- Emulsifiers for polyvinyl acetate emulsions
- Water-resistant adhesives and binders
- Hydrogels
D Polymer Uses (Conceptual Illustrations)
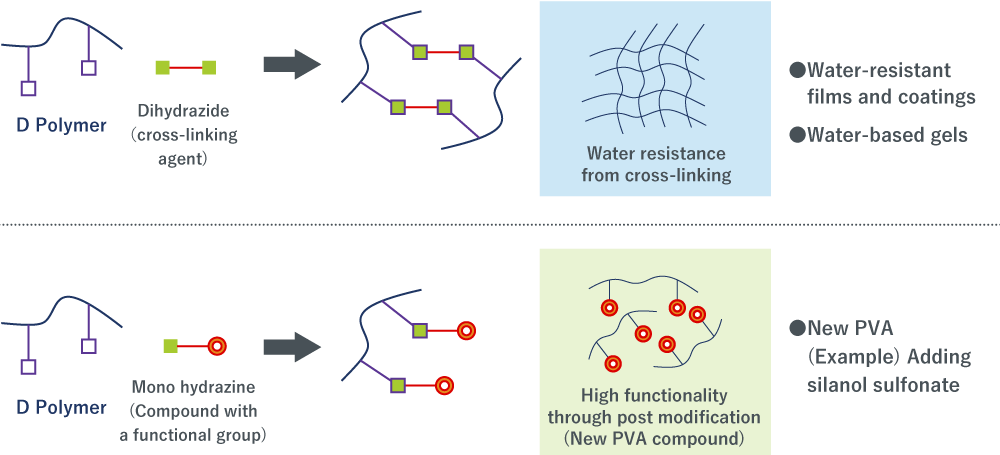
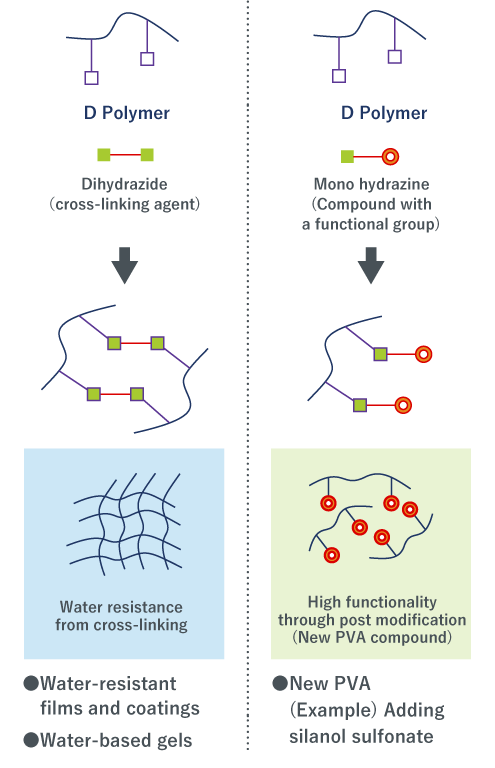
Cross-linking Agents
The carbonyl groups in D Polymer react efficiently with hydrazide and amino groups. Consequently, compounds bearing multiple hydrazide or amino groups are effective as cross‑linkers. Notably, hydrazide-based cross‑linkers enable cross‑linking at room temperature without additional heating.
| Cross-linking Agent | Water Resistance of Cross-linked Film |
Pot Life※ |
|---|---|---|
| Adipic dihydrazide (ADH) | ◯ | Approximately 24 hours |
| Ethylenediamine | △ | Over 7 days |
※5% aqueous solution of DF-17 with cross-linking agent (ADH) (5wt%/D Polymer) stored at 20˚C.
Water-resistant Properties of Cross-linked Films
When combined with an appropriate cross‑linking agent, D Polymer forms films that remain insoluble even in boiling water. This makes it highly suitable for water‑resistant overcoat layers on heat‑sensitive papers.
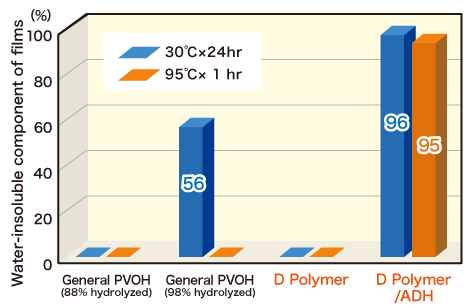
Film preparation conditions
Procedure: Cross-linked films were made by drying the mixture solution of D Polymer and cross-linking agent at 20˚C, 65%RH for 48 hours.D Polymer: DF-17
Cross-linking agent: Adipic dihydrazide (ADH) 5%/PVOH
Evaluation Procedure
The amounts of water-insoluble components were measured after the films were soaked in water at 30˚C for 24 hours or at 95˚C for 1 hour.
Stability of the Aqueous Solution of D Polymer with Cross-linking Agent
The aqueous solution of D Polymer with cross-linking agent experiences viscosity changes over time, eventually leading to gelation. However, by adding certain agents such as isopropanolamine and acetone, the “pot life” can be extended significantly–to several months–without compromising the water-resistant properties.
| Cross-linking Agent (%/PVOH) | Additives (%/PVOH) | Pot Life※ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adipic dihydrazide | Isopropanolamine | Acetone | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | A few hours |
| 0 | 10 | 3 days | |
| 2 | 0 | 13 days | |
| 2 | 10 | 60 days | |
※10% aqueous solution of DF-17 with cross-linking agent (ADH) (5%/PVOH) stored at 20˚C.
Surface Tension of D Polymer
| D Polymer | General PVOH | |||
| Grade | DF-17 | DM-17 | JF-17 | JM-17 |
| Hydrolysis (mol%) | 98.5 | 96.5 | 98.5 | 96.5 |
| Surface Tension (mN/m)※ | 57 | 51 | 66 | 60 |
※Method: Pendant drop, Concentration: 0.2%, Temperature: 20˚C.
Specialty POVAL Anion Modified POVAL [A Polymer]
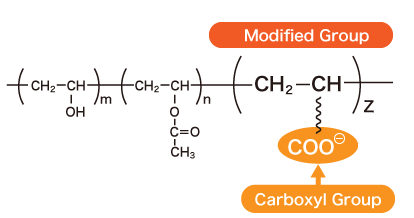
A Polymer is a modified POVAL containing carboxyl groups in addition to hydroxyl and acetate groups. Due to the presence of these anionic functional groups, it exhibits enhanced water solubility compared to general POVAL and enables applications that utilize the reactivity of the carboxyl groups.
Structural Formula
Grade and Quality Specifications
| Grade | AP-10 | AP-17 | AF-17 | AHF-17 | ALT-17 |
| Hydrolysis (mol%) | 88~90 | 96.5 or more | 92 or more | 91~93 | |
| 4% aq. Viscosity (mPa·s) | 11±1 | 28±3 | 30±3 | 30±7 | 25±5 |
| Volatiles (%) | 7.0 or less | ||||
| Sodium Acetate (%) | 3.0 or less | ||||
Characteristics
- Highly soluble in water compared to general POVAL.
- Water-resistant properties achievable through reactions involving carboxyl groups.
- Minimal foaming in aqueous solutions.
- Excellent viscosity stability in aqueous solutions.
- Superior adhesion to polyester and metals.
- Forms complexes with specific metallic salts (e.g., aluminum sulfate).
Applications
- Water-soluble films
- Water-resistant coatings in combination with cross-linking agents
- Sizing agents for paper
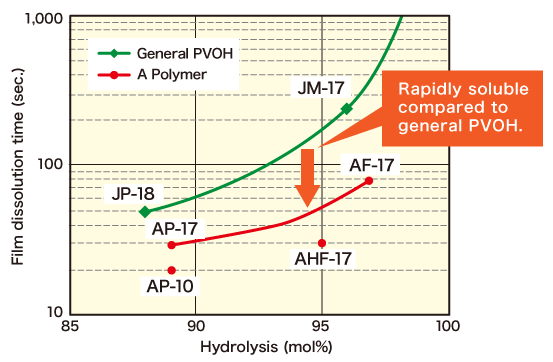
Water Solubility of Films
Due to its higher water solubility compared to general POVAL, A Polymer is suitable for various water-soluble films, such as unit-dose packaging for laundry and dish detergents.
Film preparation conditions
Films were made by drying the aqueous solution of A Polymer at 20˚C, 65%RH for 48 hours.
Evaluation Procedure
Film dissolution time was measured after the films (thickness: 40μm) were soaked in water at 20˚C.
Cross-linking Agent
| Cross-linking Agent | Water Resistance of Cross-linked Film |
Pot Life※ |
|---|---|---|
| Polyamide epichlorohydrin (PAE) resin | ◯ | Approximately 48 hours |
※5% aqueous solution of ALT-17 with cross-linking agent (PAE) resin (5%/PVOH) stored at 20˚C.
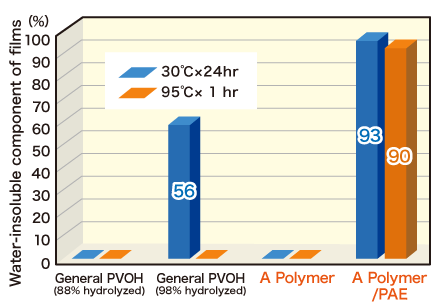
Water-resistant Properties of Cross-linked Films
Cross-linked films of A Polymer with PAE resin are insoluble even in hot water. For water-resistant films, we recommend the newly commercialized ALT-17 grade.
Film preparation conditions
Procedure: Cross-linked films were made by drying the mixture solution of A Polymer and cross-linking agent. Drying process: (i) 20˚C, 65%RH for 2 days,
(ii) 65˚C for 3 hours. A Polymer: ALT-17 Cross-linking agent: Polyamide epichlorohydrin (PAE) resin 10%/PVOH
Evaluation Procedure
The amounts of water-insoluble components were measured after the films were soaked in water at 30˚C for 24 hours or 95˚C for 1 hour.
Specialty POVAL Other Modified POVAL
JVP is developing modified POVAL with the following characteristics and is seeking applications for them. We specialize in producing products that meet customer needs. Please contact us if you are interested.
Hydrophilic PVOH
This non-ionic hydrophilic group is used to make PVOH hydrophilic and it is flexible.
Hydrophobic PVOH
This PVOH has a long-chain alkyl group. It has high viscosity even at lower concentrations and exhibits thixotropic viscosity.
Ultra water-soluble PVOH
This PVOH is more water-soluble than exiting PVOHs.
Other
JVP truly wishes to meet the needs of customers who would like us to add a particular functional group to PVOH.
Please let us know your needs.

